| BIOCHEMICAL DEFICIENCY  DIAGNOSIS Gene  |
SIGNS & SYMPTOMS Neurological  |
THERAPY Treatment  |
THERAPY Treatment  |
| General Resources |
Literature Resources |
Patient Resources |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
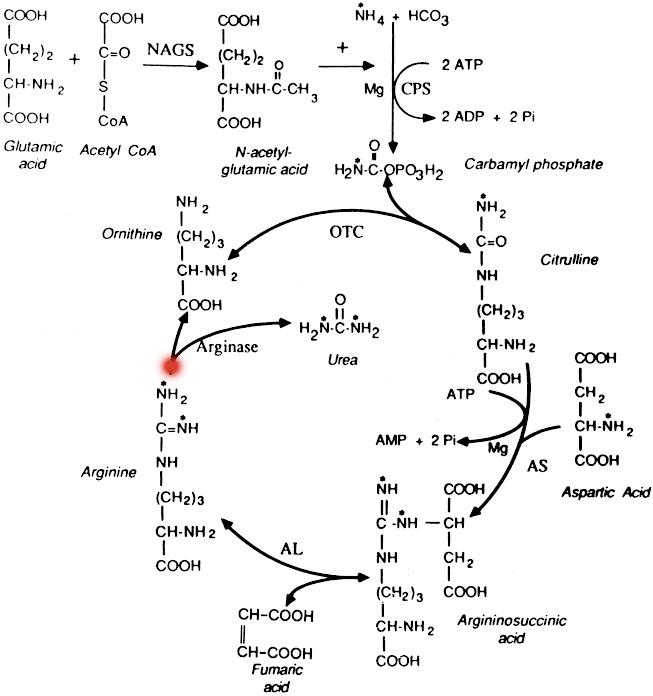
| BIOCHEMICAL DEFICIENCY  DIAGNOSIS Gene  |
SIGNS & SYMPTOMS Neurological  |
THERAPY Treatment  |
THERAPY Treatment  |
| General Resources |
Literature Resources |
Patient Resources |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
